How to Write a Restaurant Business Plan Template
- Michael Jones

- Apr 12, 2023
- 10 min read
Learn how to write an effective restaurant business plan with a step-by-step guide and template. This blog provides a comprehensive guide to creating a restaurant business plan template that entrepreneurs can use to start a successful restaurant.
Restaurant Management

Starting a restaurant may be a thrilling and gratifying business venture, but it's crucial to do it with a well-thought-out strategy. A well-written business plan not only aids in raising capital and attracting investors but also offers a road map for achievement. An essential tool for company owners in the food service sector, a restaurant business plan covers everything from defining your target market to creating a marketing strategy and financial predictions.
Therefore, if you’re thinking about opening a restaurant, it’s essential to put together a business plan. An ideal restaurant business plan template should contain an executive summary, company description, market analysis, marketing plan, operations plan, and financial plan.

What is a Restaurant Business Plan?
A restaurant business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the details of a proposed or existing restaurant business. The executive overview, firm description, market study, marketing plan, operations plan, and financial plan are typical elements that are included. A well-written restaurant business plan template aids entrepreneurs in goal-setting, market segmentation, competitor analysis, and the development of a strategy for achieving profitability. It acts as a guide for the whole operation, from idea creation to day-to-day operations, and it makes sure that every facet of the company is in line with the overarching vision and objectives. For obtaining funding, luring investors, and eventually succeeding in the food service sector, a restaurant business plan is a crucial instrument.
The Importance of a Restaurant Business Plan
A restaurant business plan is an indispensable tool for entrepreneurs starting a new restaurant or growing an existing one. The plan serves as a blueprint for the business, outlining key strategies for success in a highly competitive industry. By following a well-crafted business plan, entrepreneurs can focus their efforts on the most crucial aspects of the business and avoid costly mistakes that can derail their progress.
Moreover, a restaurant business plan is crucial for securing financing from banks, investors, or other sources. Lenders and investors want to see a comprehensive business plan that outlines the restaurant's goals, target market, competitive landscape, and financial projections. A solid business plan increases the likelihood of obtaining the funding needed to start or expand a restaurant. Additionally, the plan can help identify areas where the business needs to improve, such as marketing, staffing, or operations. By developing a plan that addresses these issues, entrepreneurs can position their restaurants for long-term success and growth, ultimately increasing their chances of achieving their goals.
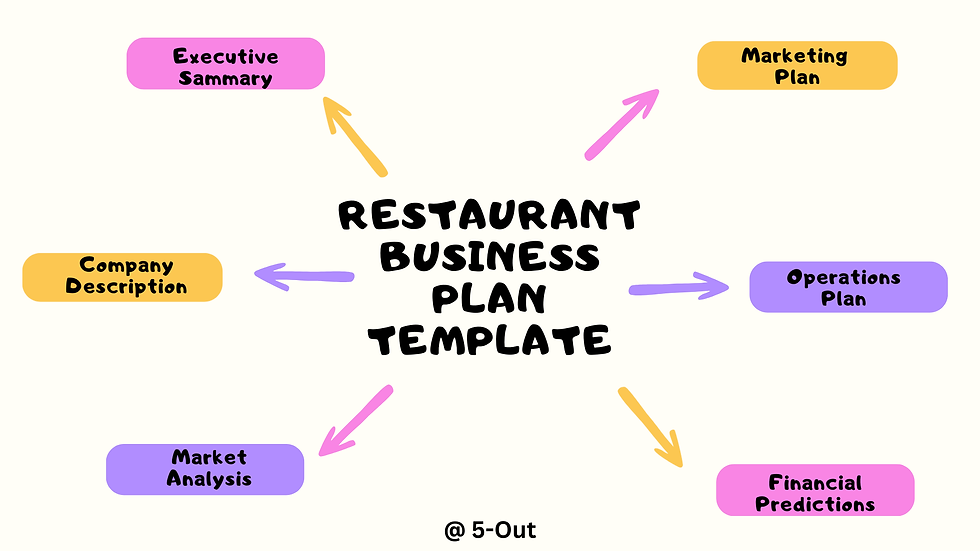
The Key Elements of a Restaurant Business Plan Template
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is a critical section of your restaurant business plan that investors and lenders will see first. It should be brief yet detailed, communicating the most important information about your restaurant in one or two pages. The executive summary includes the restaurant's overview, mission statement, target market, competitive advantage, and financial analysis and projections. It should provide an overview of your restaurant's concept, ambiance, unique features, and target market, as well as a concise summary of your mission statement and financial projections. A well-written executive summary can help grab the reader's attention, set the tone for the rest of the plan, and convey the restaurant's vision and potential for success.
2. Company Description
The Company Description section of a restaurant business plan provides a detailed overview of the restaurant's structure, location, concept, and management team. The company summary portion of a restaurant business plan is an important component of the overall business plan, laying out the overall vision for the restaurant. It also gives potential investors a glimpse into your restaurant’s concept and service style, which will help them decide if they want to invest in the project.
Type of restaurant: This section describes the type of restaurant, such as fine dining, casual dining, fast-casual, or quick-service. It should also provide details about the menu and cuisine, including any unique or specialty dishes.
Legal structure: The section detailing the legal structure of the restaurant clarifies whether the business is a sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, or corporation. It is crucial to also include information on any licenses or permits required for operation. By addressing these legal considerations within the restaurant business plan, entrepreneurs can ensure they are in compliance with applicable regulations, mitigating any potential legal issues that may arise down the line.
Location: This section provides details about the restaurant's location, including the address, square footage, and any lease or rental agreements. It should also describe the surrounding area and demographics of the neighborhood.
Concept: Within the business plan, the concept section details the restaurant's concept, encompassing its theme, ambiance, and overall atmosphere. It should also outline any unique features or amenities that differentiate the restaurant from competitors, such as a bar, rooftop dining area, or outdoor seating. By including these crucial details, entrepreneurs can effectively convey the restaurant's vision and value proposition, giving investors and stakeholders a clear idea of what sets the business apart in the crowded food industry.
Management team: The Management Team section of the restaurant business plan furnishes details about the qualifications, experience, and respective roles of the management team members within the business. It is crucial to include an organizational chart that outlines the chain of command, illustrating how the management team will work together to achieve the restaurant's goals. By highlighting the expertise and experience of the management team, entrepreneurs can instill confidence in investors and stakeholders, demonstrating that the business is well-positioned for success under the leadership of a competent and qualified team.
Staffing plan: The Staffing Plan section of the restaurant business plan details the number of employees, their roles and responsibilities, as well as the hiring process, training program, and compensation structure. By outlining these essential details, entrepreneurs can ensure they have a comprehensive plan in place to attract and retain top talent, providing customers with exceptional service and helping the business thrive in a competitive industry. By demonstrating a commitment to investing in and supporting the restaurant's staff, entrepreneurs can create a positive work culture that fosters teamwork, productivity, and long-term success.
3. Market Analysis
The Market Analysis section of a restaurant business plan provides an in-depth look at the restaurant industry, including its target market, industry trends, and competition.
Target market: The industry analysis portion of the business plan should cover your restaurant’s specific niche and target market. For example, if you plan to open a coffee shop that focuses on immersive coffee experiences, it’s critical to understand the current market and what needs your restaurant can fill. This section provides a detailed overview of the restaurant's target market, including demographic and psychographic information. It should describe the primary customer base, such as families, young professionals, or food enthusiasts, and explain how the restaurant plans to attract and retain these customers.
Market Size: To determine the size of the market, consider factors such as population numbers, demographics, and disposable income. This information will help you determine whether the market is large enough to support your restaurant concept.
Industry analysis: The Industry Overview section of the restaurant business plan presents a comprehensive overview of the industry, covering trends, challenges, and opportunities. It should also include relevant data on industry growth, consumer spending patterns, and market saturation. By thoroughly researching and analyzing the industry, entrepreneurs can gain insight into the broader context of the market, identifying potential opportunities and challenges that may affect the success of their restaurant. This allows entrepreneurs to develop a more informed and strategic approach, taking advantage of emerging trends and mitigating risks as they arise.
Competitive analysis: This section outlines the restaurant's competitors and their strengths and weaknesses. It should describe what sets the restaurant apart from other competitors in the area and explain how it plans to capitalize on these advantages. It should also identify potential threats from competitors and how the restaurant plans to mitigate them.
Market segmentation: Within the business plan, this section outlines how the restaurant intends to segment its target market, taking into account geographic, demographic, and psychographic factors. It should also include a thorough analysis of each segment's needs and preferences, along with a detailed plan of action for meeting those needs. By breaking down the target market into specific segments, entrepreneurs can tailor their marketing and sales efforts to resonate with each group, increasing their chances of success and revenue growth.
4. Marketing Plan
The Marketing Plan section of a restaurant business plan outlines how the restaurant will market itself to attract and retain customers.
Branding: The brand identity of the restaurant, including its logo, colors, and general style, is described in this section. Additionally, it should describe the restaurant's USP and how it sets itself apart from other establishments.
Menu development: This section provides a detailed overview of the restaurant's menu, including the dishes, ingredients, and pricing. It should also describe how the menu aligns with the restaurant's concept and target market.
Advertising and promotion: A summary of the restaurant's print, online, and social media marketing strategies is provided in this section. Any partnerships or agreements with local businesses or organizations must also be disclosed.
Sales strategy: The restaurant's sales strategy is covered in this part, along with pricing tactics, special offers, and promotions. It should also include the restaurant's intentions for upselling and cross-selling to boost sales.
Online presence: The restaurant's internet presence, including its website, social media profiles, and online ordering systems, is described in this section. It should also include the restaurant's goals for utilizing technology to enhance customer satisfaction and boost revenue.
5. Operations Plan
The Operations Plan section of a restaurant business plan outlines how the restaurant will operate on a day-to-day basis, including the necessary equipment, personnel, and processes to ensure a smooth operation.
Daily operations: This section outlines the restaurant's daily operations, including the front-of-house and back-of-house procedures. It should describe the roles and responsibilities of each employee, and how they work together to deliver a quality dining experience.
Supplier and vendor relationships: This part outlines the restaurant's ties with its vendors and suppliers, as well as how it chooses and oversees its suppliers. The ordering process and inventory management system for the restaurant should also be included.
Technology and equipment: The technology and apparatus utilized in the restaurant, such as the cooking tools and other technological solutions, are described in this part. A strategy for equipment upkeep and upgrades should also be included.
Inventory management: The inventory management system for the restaurant is described in this part, along with details on how inventory is monitored, ordered, and kept. Additionally, it should outline the restaurant's cost- and waste-management strategies for successful inventory control.
Quality control: The methods for ensuring food safety and cleanliness, personnel training programs, and systems for collecting consumer feedback are all included in this quality control section. It should also spell out the restaurant's long-term goals for performance evaluation and enhancement.
6. Financial Plan
The Financial Plan section of a restaurant business plan outlines the financial projections for the business, including startup costs, break-even analysis, sales forecasts, and cash flow statements. The financial plan portion of your restaurant business plan will include all the information you need to determine whether your concept is viable and feasible.
Startup costs: This section outlines the startup costs for the restaurant, including equipment, leasehold improvements, permits and licenses, and initial inventory. It should also include any financing needed to cover these costs.
Break-even analysis: The Break-Even Analysis section of the restaurant business plan describes the point at which the business will begin generating a profit, highlighting the crucial milestone of profitability. It should also provide a detailed explanation of the assumptions used in the analysis. By conducting a break-even analysis, entrepreneurs can determine the minimum amount of revenue required to cover their costs and begin generating a profit, providing a critical benchmark for measuring the success of the restaurant over time. This information is invaluable for making informed decisions regarding pricing, cost management, and revenue generation strategies, ensuring that the restaurant remains financially sustainable and profitable in the long run.
Sales forecasts: The Sales Forecast section of the restaurant business plan provides an estimate of the anticipated revenue and expenses. It should also include a clear explanation of the sales forecasting methodology employed. By projecting future sales and expenses, entrepreneurs can gain a better understanding of the financial performance of the restaurant, allowing them to make informed decisions regarding pricing, cost management, and revenue growth strategies. Additionally, a well-researched sales forecast provides investors and stakeholders with a realistic and achievable expectation of the restaurant's financial performance, demonstrating the potential for long-term success and profitability.
Profit and loss statement: A thorough profit and loss statement for the restaurant is shown in this part. It includes revenue, cost of products sold, gross profit, and net profit. It should also provide a thorough breakdown of the restaurant's costs.
Cash flow statement: The Cash Flow Statement section of the restaurant business plan provides a detailed breakdown of the restaurant's cash inflows and outflows. It should also include an explanation of the underlying assumptions used in the analysis. By preparing a cash flow statement, entrepreneurs can gain a clear understanding of the restaurant's financial health, identifying potential cash flow issues and developing strategies to manage them. Additionally, the cash flow statement provides a crucial metric for investors and stakeholders to assess the financial viability of the restaurant, demonstrating the potential for long-term profitability and growth.
Balance sheet: The Balance Sheet section of the restaurant business plan presents a snapshot of the restaurant's financial position, detailing its assets, liabilities, and equity. It should also include an analysis of the restaurant's financial health and position. By preparing a balance sheet, entrepreneurs can assess the restaurant's financial stability, identifying areas where the business may need to reduce costs or increase revenue to maintain profitability. Additionally, the balance sheet provides investors and stakeholders with a clear understanding of the restaurant's financial position, demonstrating the potential for long-term growth and profitability.

Incorporating 5-Out Sales Forecasting Software for Enhanced Restaurant Business Planning
A restaurant business plan is an essential tool for entrepreneurs looking to start a successful restaurant. It provides a detailed roadmap for the business, outlining key strategies for success in a competitive industry. From the Executive Summary to the Financial analysis, each section of the business plan plays a critical role in helping entrepreneurs achieve their goals and build a profitable restaurant.
To further enhance the accuracy and efficiency of the sales forecasting process, it is recommended that entrepreneurs consider incorporating 5-Out sales forecasting software into their business plan. This cutting-edge tool leverages the latest technology to provide accurate sales projections, enabling businesses to make informed decisions regarding labor optimization and inventory management.
By utilizing 5-Out sales forecasting software, entrepreneurs can gain a competitive edge, making data-driven decisions that maximize profitability and drive success. So if you are planning to start a restaurant business, be sure to consider incorporating 5-Out sales forecasting software into your business plan and take the first step towards achieving your goals today.
Request a demo to learn more about sales forecasting in the restaurant industry!



Comments